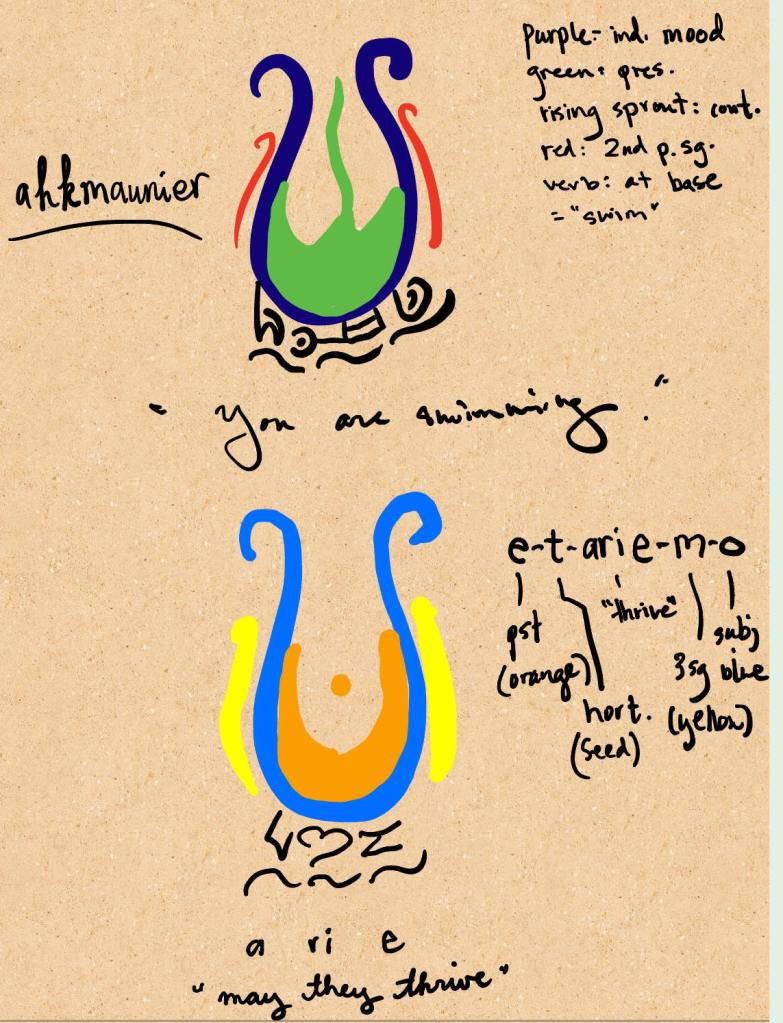
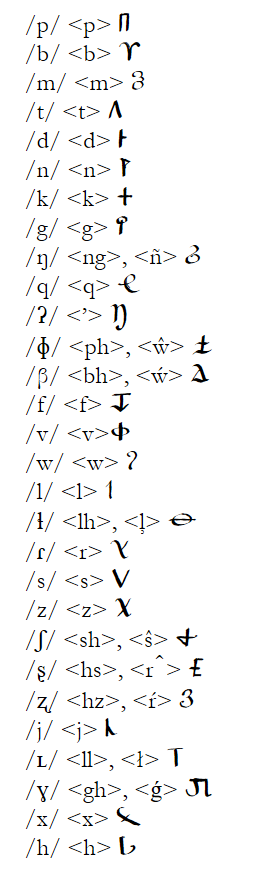Recently, I gave a presentation at 11th Language Creation Conference at the University of Maryland. I’m going to reproduce some of the content of that presentation on this blog, in the context in which it was intended: using linguistic typology to show some interesting grammatical things that can be done in conlangs, and why you, as a conlanger, should care. In the presentation, I gave an overview of different structural manifestations and semantic uses of valency-changing operations, how they appear in natural languages and how I have implemented them in my various conlangs.
Basically, a valency-change operation increases or decreases the number of core arguments in a verb. Core arguments are those that are considered necessary for a given verb: semantically, they are represented by A (agent), S (sole/subject), and P (patient). Agents are those in control of the action of a verb (broadly speaking), Patients (also sometimes called Themes) are those most affected by the verb, and Subjects or Soles are the sole argument of a verb. Languages vary in how they treat S, A, and P morphosyntactically. Nominative-accusative languages group S and A together, leaving P marked differently. Thus we get sentences like, “I bit him” and “I sleep”, in which the word “I” is used regardless of whether it refers to an A (“I bit him”) or an S (“I sleep”). Therefore, A and S are both in the nominative case and P is in accusative. Ergative-absolutive languages, by contrast, group S and P together, with A being the distinctive one. S-P are usually in the absolutive case, while A is in the ergative case. The distinction of these core argument groupings is called the verbal alignment or morphosyntactic alignment of a language.
Morphosyntactic alignment plays somewhat into valency change. When we use a valency-changing operation, we are manipulating the core arguments of a verb. Ultimately, the way a language treats core arguments becomes relevant when we fiddle with those core arguments.
First, I will outline two broad categories I will cover in this blog post series. The first is (1) valency-decreasing operations and the second is (2) valency-increasing operations. I actually hope to cover more of each than I was able to in just 20 minutes of slides and speaking for the presentation version of this essay. Ultimately, I’ll discuss: causatives, applicatives, passives, antipassives, anticausatives/middle voice, and reflexives/reciprocals. Some of these categories may overlap to a greater or lesser degree, depending on the language. It’s also true that convention often dictates the terminology used for these categories in the traditions of specific languages. I’ll try to be as explanatory as possible when describing each feature.
For now, I’ll start off with causatives, the first valency-increasing operation.
Simply put, causatives add another core argument to a verb, by inserting a causer and turning either an A or S into a causee, one who is caused by the causer to do the action. See for example, the English example below.
‘Joshua ate the spaghetti’ –> ‘I made Joshua eat the spaghetti’
The first sentence is transitive, wherein the A (Joshua) eats the P (spaghetti). In the second sentence, I use a causative (a periphrastic one that uses the verb make), thereby adding another core argument to the verb eat. “I” is now the causer, “Joshua” is the causee, and “spaghetti” is still a P undergoing the action of being eaten.
Languages vary morphosyntactically in the ways they do causatives. Some are periphrastic or analytic, as in English. Another example is in French:
‘J’ai fait manger les spaghettis à Joshua’
1s.S-aux make.pstprt eat the spaghetti to J.
‘I made Joshua eat the spaghetti’
Note how in the French version of this sentence, the causee is now marked as an oblique, preceded by the preposition à ‘to’. This one of two major strategies languages use to show that a former A/S is now no longer such, due to the addition of the causer. The causee can either be marked oblique, as above, or it may be marked the way other P nouns are. In the latter case, we see examples like that in Sanskrit below, in which the causative allows two accusative-marked nouns to coexist in one clause.
Rama-m veda-m adhyapa-yate
Rama-acc veda-acc learn-caus
‘He teaches Rama the Veda’ (Literally: ‘He makes Rama learn the Veda.’)
In the above sentence, you can see that this causative construction allows two nouns to be marked accusatives. One is the causee (Rama), and one is the object of the verb (the Veda) that the causee is being caused to perform .
The above example also shows us that causatives can be morphological, or marked directly on the verb with some morpheme. This is also a cross-linguistically very common way of doing causatives. Sometimes, languages differentiate between which causatives apply to transitive verbs and those apply to intransitive verbs. See the examples below from Turkish. ‘die’ is an intransitive verb, and thus when it is causativized, it gets the -dür causative.
Hasan öl-dü
H. die-pst
‘Hasan died’
Ali Hasan-t öl-dür-dü
A. H. -acc die-caus-pst
‘Ali killed Hasan’
However, if the verb we start out with is already a transitive verb, a different causative morpheme is used, the -t morpheme. The first sentence below shows a regular transitive sentence, “The director signed the letter”. Then we see how such a sentence could be causativized: “The dentist made the director sign the letter.”
Müdür mektub-ü imzala-dı
director letter-acc sign-pst
‘The director signed the letter’
Dišçi mektub-ü müdür-e imzala-t-tı
dentist letter-acc director-dat sign-caus-pst
‘The dentist made the director sign the letter’
Causatives can also be lexical. That is, they can be represented by totally separate lexemes or words. This is not an instance of a word being modified by a morpheme, but something else entirely. English has several examples of this, notably the die and kill pair. ‘kill’ is a causative of ‘die’. Another such pair is eat and feed. A cross-linguistic tendency noted in Haiman (1983): within languages that have multiple strategies for creating causatives, lexical causatives tend to show a greater level of control and directness of causation than morphological causatives, which in turn show a greater degree of such than analytic causatives.
Below, I’ll provide a few examples of ways I have created causatives in my conlangs. The first example comes from Seloi. This somewhat isolating language has an analytic causative. The particle here is sli. It was, historically, a verb, and it still sits in a verbal position in the clause, but it lacks any other trappings of a real verb, such as tense, aspect, or modality. Therefore, it can be said to be fully grammaticalized.
Vali sli na te-keva te-koi ai Iskila
3s.m caus for def-woman come-fem loc Iskila
‘He is having the woman come to Iskila’
Note how in this construction, the causee is demoted to an oblique role, prefaced by the preposition na ‘for’.
In Rílin, morphology is the main way to implement a causative. The prefix xa- increases the valency of a verb by adding a causer. For example, the intransitive verb psílha [‘psiɬa] means ‘to bleed’. xapsilha is ‘to make bleed’, with an extended meaning ‘to injure, to hurt’. lhesti [‘ɬɛstɪ] is ‘to listen’, can be either transitive or intransitive, while xalhesti is ‘to make listen’ and by extension, ‘to warn, to make heed’. So we can increase the valency of these verbs with xa-, regardless of whether they are intransitive or transitive to begin with. Some of the resulting meanings of the causative forms have become idiomatic, such as zaryxía [zary’xia] ‘to rust’ and xazaryxia ‘to renounce’. The latter has moved completely into its metaphorical meaning, which has now become its primary sense.
Rílin also has a number of lexical causatives. zansa ‘to kill’ has no etymological relation to lemua ‘to die’. But zansa replaces any instance of *xalemua, which is not attested. Similarly, saísa ‘to rise’ and hare ‘to raise’ have no structural or etymological relationship, but the latter can be said to be a (semantically) causative form of the former.
Karkin, another of my conlangs, has an active-stative aligment system. Karkin has four causative morphemes, each of which shows a different implication about harm and benefit on the part of the causer and/or causee.
Type 1: Karkin causative Type 1 implies a benefit for the causee of the action (the one who was caused to act).
məl-a-i ava-a mi shoʔonthe-‘ə pa ʃtuxtə-peq-aː
mother-1S.POSS.A father-1S.POSS to river-P PART cross-CAUS-PST
‘My mother made my father cross the river (it was good for him/he liked it)’
You can identify this causative by use of the morpheme –peq– preceding the tense morpheme at the end of the verb. Avaa ‘my father’ is in an oblique case, shown by the postposition mi.
Type 2: Karkin causative Type 2 implies harm or misfortune toward the causee.
məl-a-i ava-a-ʔə shoʔonthe-ʔə pa ʃtuxtə-vur-aː
mother-1S.POSS.A father-1S.POSS-P river-P PART cross-CAUS-PST
‘My mother made my father cross the river (it was bad for him/he didn’t want to)’
This kind of causative is marked by the verbal morpheme -vur-. It also marks the causee, avaa, with a patient marker instead of an oblique one: -ʔə.
Type 3ː Karkin causative Type 3 implies neutrality for the causee as to benefit/harm.
məl-a-i ava-a mi shoʔonthe-‘ə pa ʃtuxtə-χe-aː
mother-1S.POSS.A father-1S.POSS to river-P PART cross-CAUS-PST
‘My mother made my father cross the river (it was neutral)’
This kind of causative is marked by the verbal morpheme –χe-. The causee is marked obliquely with –mi-.
Type 4: The final causative type implies mutual benefit between causer and causee.
məl-a-i ava-a mi shoʔonthe-‘ə pa ʃtuxtə-li-aː
mother-1S.POSS-A father-1S.POSS to river-P PART cross-CAUS-PST
‘My mother made my father cross the river (it was mutually beneficial)’
This type of causative uses the –li– morpheme and marks the causee with oblique mi.
~
I’m going to end or at least pause my discussion of causatives. Next time, I will likely write about applicatives. This is one subject I didn’t have time to discuss in my presentation of this topic, so I’ll be pleased to put my thoughts into words.